
Export of the extracted data and images.Īccounts payable automation is a technology-driven approach to invoice processing.

Identification of the vendor and business unit associated with the invoice, 3. Import of the images through scanning or email, 2. The typical workflow is a four-step process beginning with 1. If there are other people involved in the approval workflow, email alerts to them will also be automatically generated. Workflow steps can be configured such that the responsible person will then receive an email alert so that he or she can approve the invoice. This matching process can compare just the invoice data with that shown on the purchase order or be expanded to include a deeper level that looks at the receiving documents. In an automatic process, once the data is extracted or captured from the invoice the data is sent into the system for automatic matching against the purchase order.
#INVOICES DEFINITION SOFTWARE#
Most automation software today integrates into common organizational ERP systems such as SAP, Microsoft, and Oracle. The benefits of an automatic processing workflow may include reduced human error, on-demand reports, and data resilience. The different fields on an invoice can also be defined into the software so that it remembers which fields it should capture and register into the ERP systems, for instance, the purchase amount, the quantity, the supplier name, the supplier code, and so on. The automation software then converts the invoice's scanned image into a text-researchable document. This means that at arrival of the invoice, the same accounts payable clerk will only need to scan the invoice into an automation software. Technology has long enabled the automation of invoice processing from arrival to post.
#INVOICES DEFINITION MANUAL#
From there, a voucher can be created and the payment can be issued.Ī manual invoice process can sometimes exceed 15 steps before the final posting is done. Once the invoice has been approved and there have been no variances, the invoice is posted into the accounting system. This, of course, also differs from organization to organization. If the amount invoiced exceeds a certain amount that is limited by the organization, the superior of that person may have to approve the invoice as well. If the amount is right and the goods have arrived, the responsible person will have to approve the invoice by signing off on it. (This helps protect against fraud and unauthorized transactions.) If there was a purchase order created during procurement, the invoice must then be matched against the purchase order to confirm that the amount that is being paid is correctly stated on the invoice. This is normally the person who has placed that order. Once the invoice is classified, it is forwarded to the AP processor who is responsible for the particular invoice. The definition of invoice categories is usually unique to a specific organization.

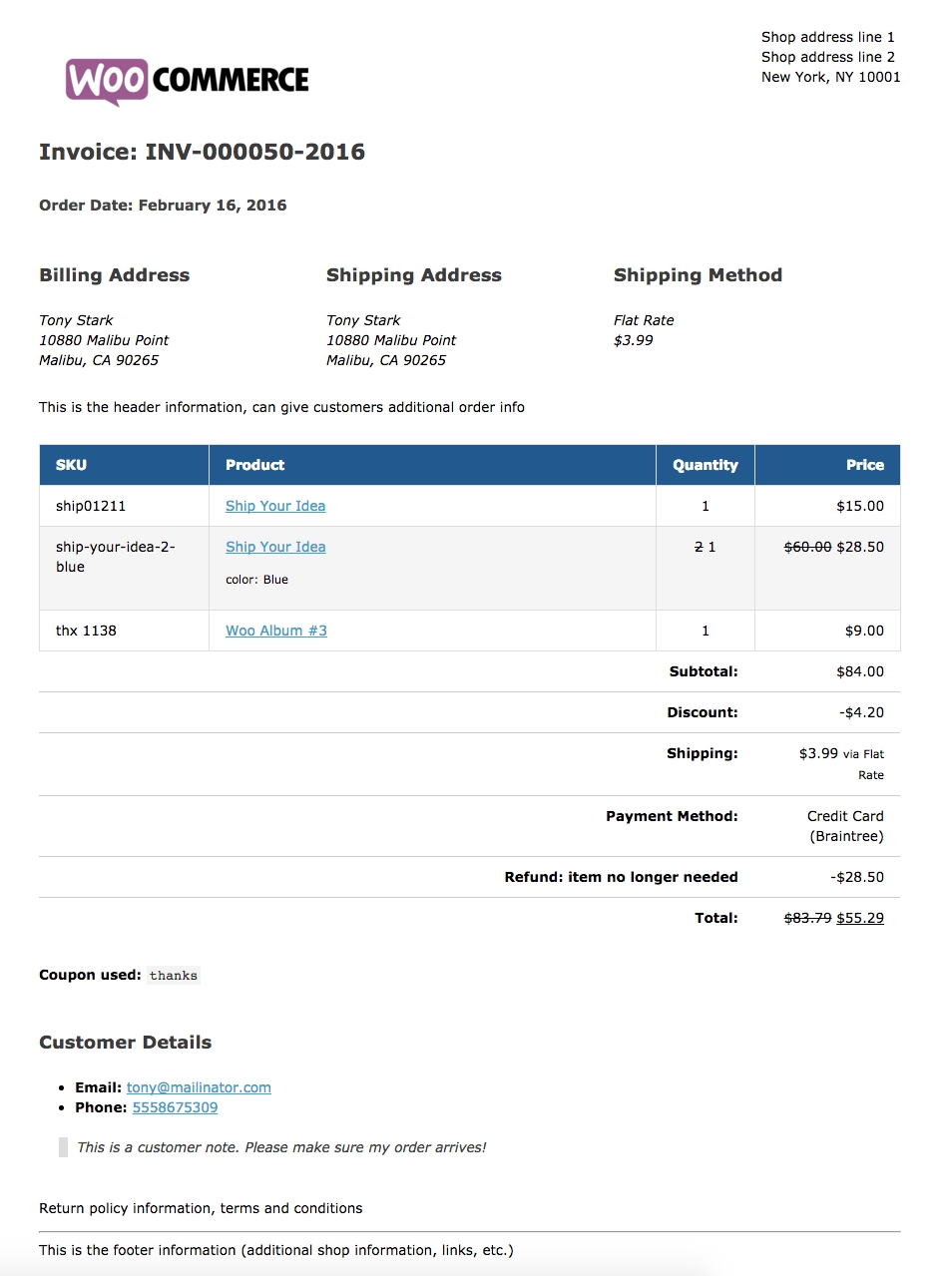
Then the clerk classifies and sorts the invoice into various categories (e.g., by vendor, by transaction type, or by department). Once an invoice arrives, the accounts payable clerk must ensure that the document is indeed an invoice. Invoices can be sent via email, postal mail, fax, or EDI. The process usually begins when a supplier's invoice is received. The process in which a supplier invoice is validated and paid is also known as the purchase-to-pay cycle. In general, both types of invoices are processed by a company's accounts payable department. Some companies also have unique requirements based on the type or dollar amount of a transaction. It is common to have one approach for PO-based invoices, and another for non-PO invoices. Most organizations have clear instructions regarding the way that they should process incoming invoices. Invoices that do not have an associated request (non-PO invoices). Invoices associated with a company's internal request or purchase order (PO-based invoices) andĢ. In general, invoices are grouped into two types:ġ. Invoice Processing : involves the handling of incoming invoices from arrival to payment.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
